
| Date | May 5th, 1789-9th of November, 1799 |
| Notable People Who Influenced The Revolution | Voltaire, Montesquieu, John Locke, Thomas Hobes, Thomas Jefferson |
| Further Reading | The 3 Things That Led To The Scientific Revolution |
On May 5th, 1789 one of the most important events in history took place. King Louis XVI called the estates general of France to meet to discuss increasing taxes on the general population of France to help forestall French bankruptcy. This was the start of what we now call today the French Revolution and there are 3 major ways in which in changed the world.
When we discuss the French Revolution it is important to note the 3 ways in which it changed the world forever. First, the French Revolution marked the beginning of the end of absolutist monarchy government in Europe. Second, the French Revolution began the process of universal abolishment of slavery in the west. Third, the French Revolution marked the end of the control of the Catholic Church over matters of state in Europe.
Here at The History Ace, I strive to publish the best history articles on the internet. If at the end of this article you enjoyed it then consider subscribing to the free newsletter and sharing it around the web.
Without further ado, here are the 3 ways the French Revolution changed the world.
The French Revolution Marked the End of Absolutist Monarchy in Europe
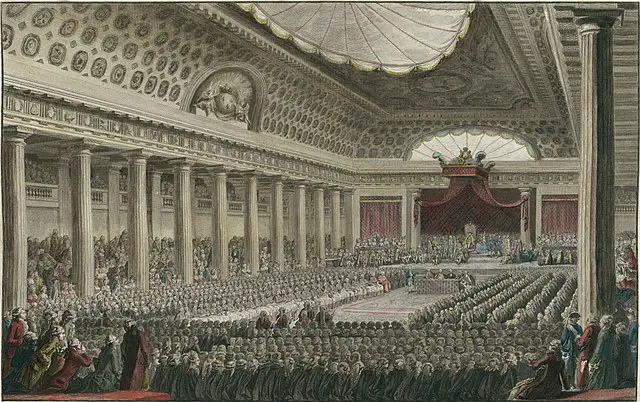
One of the main ways in which the French Revolution forever changed the world is that it marked the beginning of the end of the absolutist monarchy style of government in Europe.
From the 8th century up until the French Revolution at the end of the 18th kings and queens ruled all of Europe. England, France, Russia, Spain, Italy, and Germany all had their own kings and queens who held nearly complete control over their individual realms. While these rulers often had a form of parliament in effect they held complete control over the rules of their territory. The French Revolution forever changed this.
On May 5th, 1789, King Louis of France called together the Estates General for the first time in over a century. This body of government acted as a form of parliament that could provide guidance for the ruler. There were 3 bodies of this government; the first was the ruler and nobility, the second was the clergy, and the third was the general people.
However, the first two estates always voted in unison which negated any power that the common person of France had over their own government. In 1789 France was falling apart from centuries of debt piled up. The third estate was already taxed to the point of poverty and now they could not vote to change anything as the clergy and nobility would vote against them.
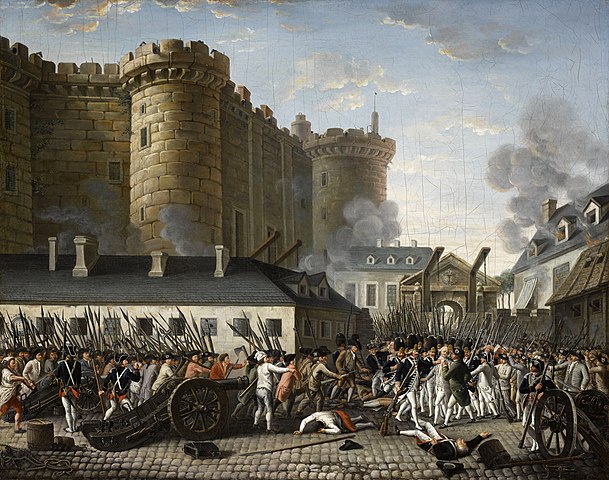
At the top of this mess was King Louis who spent his life eating good food and living in luxury while his people starved. On the 14th of July, the people of France had enough and stormed the ancient French prison of the Bastille located in Paris. As a symbol of the French Regime in the heart of the city, the people of France had the Bastille dismantled brick by brick to demonstrate their resolve to remove the monarchy from power.
This was the beginning of the end of absolutism monarchy in Europe. From 1789 up until the modern day all kings and queens would slowly have their power stripped from them and handed back to the people. Within a century later most of Europe had some form of democratic government and an elected body of people.
As such one of the main ways the French Revolution changed the world was by effectively marking the end of the absolutism monarchy form of government. Today when we see a democratic form of government in Europe we can thank the people of France.
The French Revolution Marked the End of Slavery in the West

One of the major ways in which the French Revolution changed the world was by marking the end of slavery in the western world.
The French Revolution was fought over the concept of universal equality among all men. The common French person in 1789 was tired that they held virtually no power over their own government and life. This was because they were not citizens of France but rather subjects of the French King. As such one of the main reasons that the French Revolution happened was to provide universal suffrage for the French people. For the first time in the history of France, the power over government was handed to the people.
The writer of the first French Constitution was Gilbert du motier, Marquies de Lafayette; Lafayette is how we know him today. He fought in the Americas during the American War of Independence and upon returning back to France was a major figure in the French Revolution. Assisted by Thomas Jefferson Lafayette would pen the basics of the French Constitution which included a universal suffrage policy for all French citizens.
Saint-Just was asked to amend the constitution for the first French Republic in 1793. Part of this amendment was to include a formal abolition of slavery in all of France and her colonies in the new world. This was a major step towards abolishing slavery as up until this point in time the western world had nothing preventing the enslavement of people as part of their constitution.
One of the main parts of this universal suffrage was that all French people were free and equal. However, due to the nature of the French Revolution as an ongoing revolution, the policy of outlawing slavery did not take effect until 1794. This outlawing of slavery as part of universal suffrage was the first out of any western constitution during the modern era. It did not take long for this policy to take hold in other countries and by the early 19th century the Atlantic Slave Trade was nearly completely gone.
As such one of the major ways in which the French Revolution changed the world forever was by putting in place the first formal abolition of slavery as part of their constitution. This universal suffrage set in motion a series of events that would result in the complete abolishment of slavery in western countries by the 20th century.
The French Revolution Marked the End of the Control of the Catholic Church Over Matters of State in Europe

For nearly 200 years before the French Revolution, the Catholic Church of Europe had been fighting to retain control over the election of officials of state across Europe. From 1517 up until the French Revolution, the Catholic Church as losing this battle as more and more nations became independent from the power of the church.
The last bastion of the power of the Catholic Church to appoint government officials in Europe was France. In 1789 the French Revolution marked the official end of formal Catholic church control over matters of state in any major European country.
The reason the French Revolution targeted the removal of the clergy from the powers of state was that the Clergy would always side with the nobility during government meetings and processes. In turn, the nobility would provide salaries, power, and land for the clergy in France. This symbiotic relationship worked together to sideline the power of the average French person.
As a result of this one of the main purposes of the French Revolution was to fracture the power that the Catholic church had over the electing and voting of the French government. During the French Revolution, the people of France seized all land owned by the Catholic Church. On top of this, the people of France abolished the policy that they would automatically be taxed 10% of their income to the church to pay for certain social welfare programs. Instead, the state would directly tax the people and provide for the social well-being of the people.
In 1790 forced employment in religious orders and monasteries was abolished by the First French Republic. Priests and nuns were given the option to return to their private lives as French citizens instead of staying with their religious order.
Finally on July 12th, 1790 the First French Republic passed the Civil Constitution of the Clergy which made all clergy members in France members of the French Republic. They would receive salaries and be loyal to the French nation instead of the Pope in Italy.
This law has since been overturned but the power of the Catholic Church over Europe has since been forever fractured because of the French Revolution. Today we have independent nations in Europe because of the French Revolution and as such, this is one of the major ways in which the French Revolution changed the world.
Conclusion
There you have it; the 3 major ways in which the French Revolution changed the world forever.
I hope you enjoyed this article. Here at The History Ace, I strive to publish the best history articles on the internet. Feel free to subscribe to the free newsletter and share it around the internet; every share helps tremendously so thank you.
Further, you can check out some of the other articles below.
-
How The American Revolution Changed The World

Here is how the American Revolution changed the world. Many people are not aware of just how important this event actually was.
-
Why The Roman People Loved Chariot Racing

Why did the Roman people love chariot racing? Well it all comes down to these 3 reasons.
-
The Design and Color of Roman Chariots

What was the design and color of Roman Chariots? Were they faster or slower then normal chariots? Well here is everything!